 |
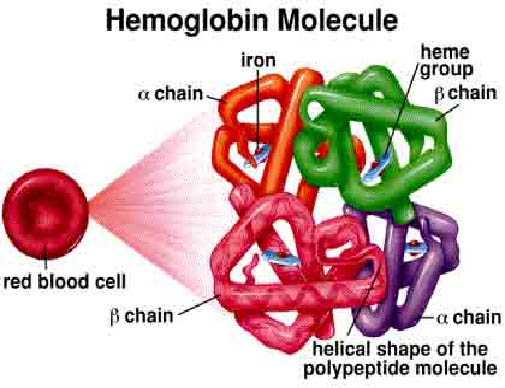
| Haemoglobin molecule |
v Haem is actually an iron containing compound of porphyrin class which forms the non – protein of haemoglobin and some other molecule.
v Haem synthesis occur largely in the mitochondria.
HOW ABOUT GLOBIN??
v Superfamily of haem containing globular protein and involve in binding, transporting oxygen.
v Globin synthesis occurs in the polyribosome.
WHAT IS HAEMOGLOBIN?
v Haemoglobin is a protein molecule in the red blood cell that carries oxygen from lungs to the tissues and return carbon dioxide from tissue to lungs to be exhaled out. Molecular weight of the haemoglobin are about 68000 and comprise one third of a red cella. Haemoglobin is formed from the combination of haem and globin.65% of the haemoglobin will be synthesised in the erythroblast and the remaining 35% at the reticulocyte stage. A normal person would have haemoglobin HB-A that consist of four polypeptide chains a2B2 each with its own haem group.
HAEMOGLOBIN SYNTHESIS
v Haem synthesis begins with the
condensation of glycine and succinyl-CoA to form δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA). ALA then leaves the
mitochondria and form porphobilinogen through a series of reaction forms
coproporphyrinogen. This molecule then returns to the mitochondria and produce protoporphyrin.Proto-porphyrin is then
combined with iron to form haem. Haem then exits the mitochondria and combines
with the globin molecule which is synthesized in the ribosome.
Red cell destruction will occur after the life span of the red blood cell end (120 days)The cell are removed by macrophages of the reticularendothelial system in the bone marrow, liver and also spleen. This in turn leads to red cell metabolism gradually decline as enzyme are degraded and not replaced, until the cell become iron viable (the reason is unknown).The healthy red blood cells are in biconcave shape and after 120 days, the red blood cells become spherical in shape (change in morphology) resulting the spleen and other associate organs cannot recognise them and found that the cells could bring hazard to the body. The spleen then ask macrophage to destroy the cell.(terminology)
v The breakdown of the cells release these 3 components:
- Iron for recirculation via plasma transferrin to marrow erythroblast.
- Protoporphyrin which is broken down to bilirubin.
- Globin which are converted to amino acids.
The bilirubin circulates to the liver where it is conjugated to glucuronides which are excreted into the gut via bile and converted to the stercobilinogen and stercobilin (excreted in faeces). Stercobilinogen and stercobilin are reabsorbed back and excreted in urine as urobilinogen and urobilin. Meanwhile a small fraction of protoporphyrin is converted to carbon monoxide and excreted via the lungs. Globin chains are broken down to amino acid which are reutilized for general protein synthesis in the body.




